China is a very diverse country with a range of economic statuses ranging from very rich to very poor. These are China Mike’s 100% verified, no B.S. China facts about the Rich, Poor, & Inequality of China.
POVERTY & RISING LIVING STANDARDS
Between 1981 and 2005, an estimated 600 million Chinese people moved out of poverty (US$1/day) and China’s poverty rate dropped from 85% to 15%.
[World Bank report; Wikipedia “Poverty in People’s Republic of China” ]
According to China’s official statistics, between 1978 to 2007:
- China’s per capita rural net income increased from 133RMB to 4,140RMB.
- China’s per capita urban disposable income increased from 343RMB to 13,785RMB.
- Per capita rural housing space increased from 8.1 to 31.6 square meters.
- Per capita urban housing space increased from 4.2 to 22.6 square meters.
Between 1985 to 2007:
- China’s ownership of color TV per 100 families increased from 0.8 to 94.4 (rural families) and 17.2 to 137.8 (urban).
- China’s ownership refrigerator per 100 families increased from 0.1 to 26.1 (rural families) and 6.6 to 95 (urban).
Between 2000 to 2007, China’s car ownership per 100 families increased from 0.5 to 6.06.
[ China National Bureau of Statistics, 2008; China Statistical Yearbook 2008 ]
China has more people who aspire to own a car, but currently do not, than any other country in the world, according to the research company AC Nielsen.
[BBC News “Cracking China’s car market” May 17, 2007 ]
Click here for more on China’s Exploding Car Culture in China Facts: TRANSPORTATION & CARS.
Only about 20% of Chinese own a credit card, according to a CCTV survey.
[ Xinhuanet News, September 14, 2007 ]
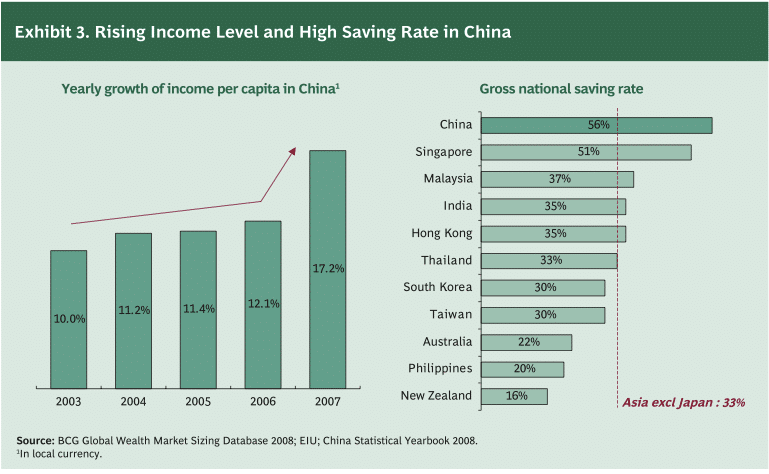
China has 38% savings rate, one of the highest in the world—due in part to the fact that there is no national safety net. Other savings rates: India (34.7%), Germany (11.7%), Britain (7%), U.S. (3.9%), Australia (2.5%).
[ Businessweek, June 10, 2010 ]
China facts: POOR & POVERTY STATISTICS
China has about 150 million people living below the United Nations poverty line of one US dollar a day.
[ Wikipedia “Income Inequality in China”; China Development Research Foundation Feb 2011 report ]
Nearly 500 million Chinese people live on less than $2 a day.
[ BBC News “Millions ‘left behind’ in rural China” May 12, 2010 ]
85% of China’s poor live in rural areas, with about 66% concentrated in the country’s west.
[China Development Research Foundation Feb 2011 report ]
99% of China’s poor live in or come from rural areas, according to national statistics, which count migrant workers in cities among the rural, not urban poor. Even if migrant workers are excluded from the rural population, 90% of poverty is still rural.
[ Wall Street Journal “Facts About Poverty in China Challenge Conventional Wisdom” April 13, 2009 ]
Over half of China’s population lives in rural areas…but they share less than 12% of the country’s wealth.
[ The Telegraph UK “China’s wealth gap the widest since economic reforms began” March 2, 2010 ]
Levels of poverty are higher and more severe in China’s western regions, but nearly half of the poor are in other parts of the country.
[ Wall Street Journal “Facts About Poverty in China Challenge Conventional Wisdom” April 13, 2009 ]
China’s poverty among ethnic minorities is two to three times higher than among the Han Chinese.
[ Wall Street Journal “Facts About Poverty in China Challenge Conventional Wisdom” April 13, 2009 ]

Up to 200 million Chinese workers and peasants suffer from occupational ailments, according to data from the Ministry of Health.
[ Wall Street Journal “Rich China, Poor Peasants” July 24, 2009 ]
China facts: MIDDLE CLASS
China’s middle class is estimated to between 100 million and 150 million people.
[ National Geographic, “China’s Middle Class” May 2008]
China has about 55 million middle-class households, according to McKinsey & Company, which wrote: “That number could more than quadruple to nearly 280 million in 2025, to account for more than three-quarters of all China’s urban households.”
[ McKinsey & Co. “Comparing urbanization in China and India” July 2010 ]
China facts: GROWING INCOME INEQUALITY

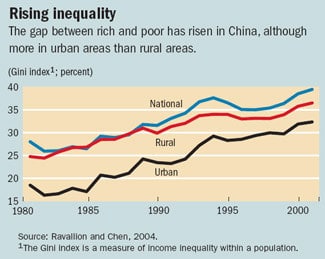
China ranks #53 worst worldwide in terms of income inequality, with a Gini index (measuring wealth inequality) of 41.5. In comparison, the U.S. ranks #40 worst with a Gini index of 40.
[ CIA World Factbook, accessed March 2011 ]
In the mid-2000s, China’s top 10 percent of the population controlled 45 percent of the country’s wealth.
[ China’s National Bureau of Statistics ]
In 2009, China’s urban per capita annual income of about US$2,500 was nearly three times that of rural residents. The gap is much more extreme in larger, wealthier cities such as Beijing ($9,085 in 2008) and Shanghai ($10,529 in 2008).
[ China’s National Bureau of Statistics ]
The average annual income in China’s cities is now more than three times the average income in the countryside, according to the National Bureau of Statistics.
China Daily, the government-run newspaper, reported that it was the widest disparity for more than three decades.
[ The Telegraph UK “China’s wealth gap the widest since economic reforms began” March 2, 2010 ]
China facts: WEALTHY & SUPER-RICH
China now has more billionaires (128 in 2011) than any other country except for the U.S. (412 in 2011).
[Forbes; Wikipedia “List of countries by the number of US dollar billionaires”]
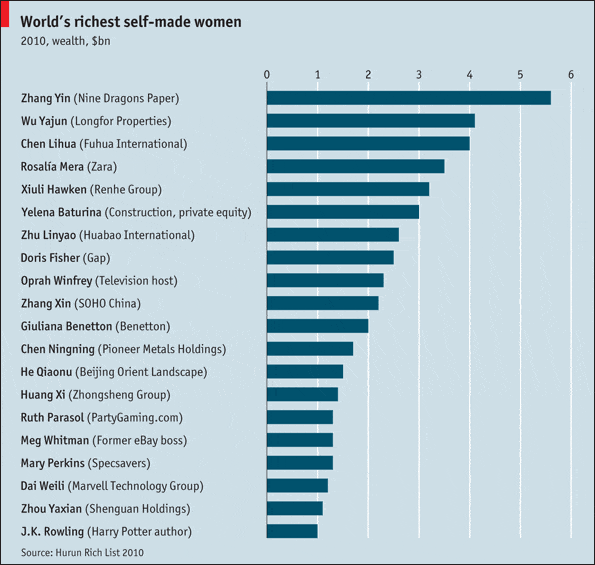
Over half of the world’s top 20 richest self-made women are Chinese, including the top three richest.
{ The Economist online “The Great Wealth of China” Oct. 13, 2010 ]
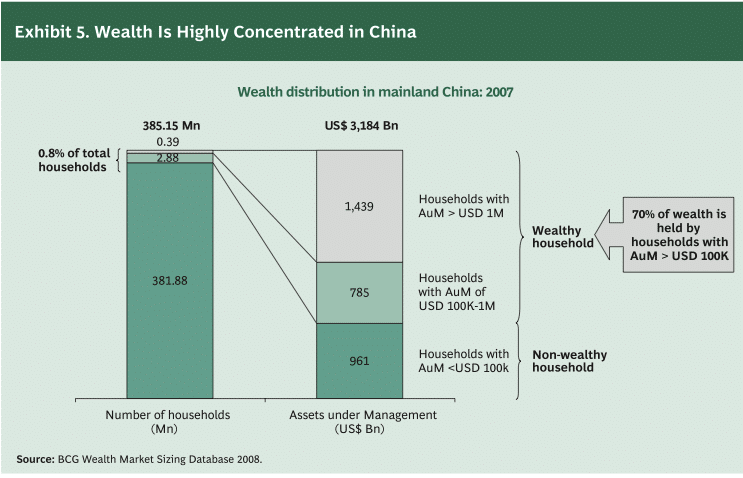
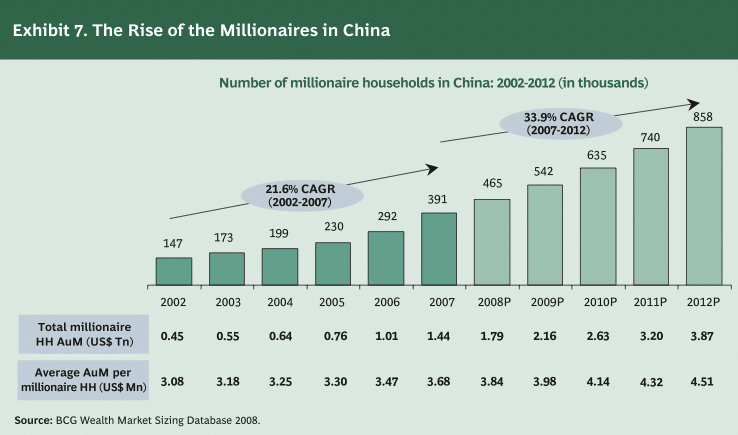
Between 2006 and 2007, the number of Chinese millionaires (in US dollars) jumped 34% to 391,000 households.
[ Boston Consulting Group 2008 report “Wealth Markets in China” ]
China has the fourth-largest number of millionaires in the world, after overtaking Britain in 2008 for the No. 4 spot and France in 2007.
[ BusinessWeek “A Rebound for China and India’s Millionaires” Oct. 13, 2009 ]
Chinese millionaires are on average 15 years younger than their overseas peers.
[CLSA investment group report, “Dipped in Gold: Luxury lifestyles in China”, Feb. 2 2011]
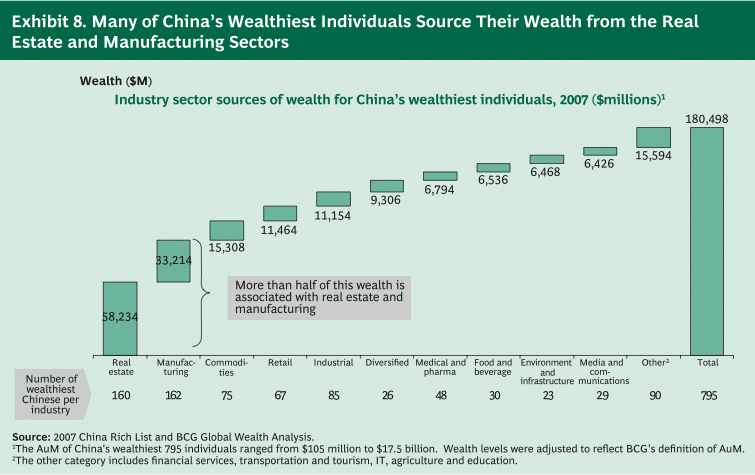
Real estate and manufacturing together make up more than half of China’s wealth creation among the richest Chinese individuals.
[CLSA investment group report, “Dipped in Gold: Luxury lifestyles in China”, Feb. 2 2011]
China facts: LUXURY GOODS MARKET
China is world’s second largest consumer market for luxury goods, behind only Japan (after passing the U.S. in 2009).
[ Wikipedia “Luxury goods in the People’s Republic of China” ]
By 2014, China’s domestic market for luxury goods will be bigger than Japan’s.
[CLSA investment group report, “Dipped in Gold: Luxury lifestyles in China”, Feb. 2 2011; The Economist “China’s luxury boom: The Middle Blingdom” Feb. 17, 2011 ]
China is expected to be the world’s largest luxury good market for the next decade.
[CLSA investment group report, “Dipped in Gold: Luxury lifestyles in China”, Feb. 2 2011]
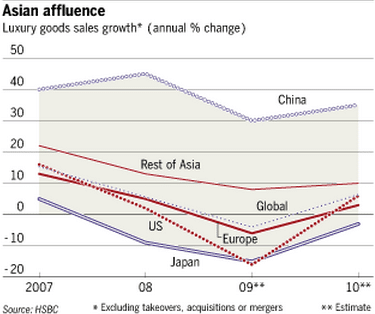
Luxury goods sales in China is expected to rise 25% annually over five years (2011-2016), which is twice as fast as overall consumption growth in China (11%). “Prosperous Chinese are less shy about flaunting their wealth than people in other countries. On the contrary, many believe they must show off to be taken seriously.”
[CLSA investment group report, “Dipped in Gold: Luxury lifestyles in China”, Feb. 2 2011; The Economist “China’s luxury boom: The Middle Blingdom” Feb. 17, 2011 ]
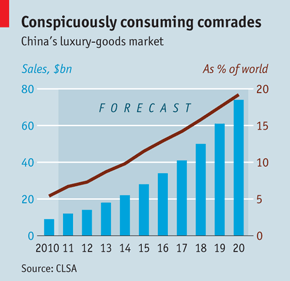
By 2020, China’s domestic market will account for 19% of global demand for luxury goods.
[CLSA investment group report, “Dipped in Gold: Luxury lifestyles in China”, Feb. 2 2011; The Economist “China’s luxury boom: The Middle Blingdom” Feb. 17, 2011 ]
By 2020, China’s global share of the luxury market will triple to 44% if luxury goods bought by Chinese outside China are included with domestic purchases.
[CLSA investment group report, “Dipped in Gold: Luxury lifestyles in China”, Feb. 2 2011; The Economist “China’s luxury boom: The Middle Blingdom” Feb. 17, 2011 ]
About 55% of the luxury goods bought by Chinese people are bought outside mainland China. “This is partly because of those high tariffs, which can top 30%. But it is also because counterfeiting is rife. Ask a well-heeled Chinese lady about her new handbag and she is quite likely to point out that she bought it in Paris. This tells you not only that she is rich enough to travel, but also that the bag is genuine.”
[CLSA investment group report, “Dipped in Gold: Luxury lifestyles in China”, Feb. 2 2011; The Economist “China’s luxury boom: The Middle Blingdom” Feb. 17, 2011 ]
By 2015, women in China are expected to account for 55% of the $9 billion luxury goods market. Chinese men have “historically been the primary consumers of luxury goods, in large part because of the custom of giving gifts to business partners and government officials”. You might be shocked to see the massive Chinese shopping centers that have all the major luxury name brands.
[ Newsweek “Chinese Women Go Shopping” Aug. 27, 2010 ]
Q: What % of Chinese women say they control the family’s purse strings? Find out in China facts: WOMEN, MARRIAGE, DIVORCE & BRIDE-NAPPING.
China is expected to overtake India as the world’s largest consumer gold market.
[ Report from London precious metals consultancy GFMS Ltd, China Gold Association]
China is Louis Vuitton’s largest market, accounting for 15% of its global sales. The Chinese also account for 28% of global sales for Swatch, 22% for Richemont, 18% for Gucci, 14% for Bulgari and 11% for Hermes.
[CLSA investment group report, “Dipped in Gold: Luxury lifestyles in China”, Feb. 2 2011; The Economist “China’s luxury boom: The Middle Blingdom” Feb. 17, 2011 ]
Shanghai has three Louis Vuitton stores.
[The New York Times “In China, Cultivating the Urge to Splurge” Nov. 24, 2010 ]
China is expected to top the U.S. as Rolls Royce’s #1 market.
[ Bloomberg, “Rolls-Royce Seeks China Sales Surge for $990,000 Cars” Nov. 29, 2010]
Luxury brands are increasingly tailoring products to the Chinese market. In 2010, the French luxury giant Hermès opened a boutique in Shanghai for its new Chinese brand, Shang Xai. BMW launched a China-only limited version of its M3 (an orange-and-black “Tiger”, for the 2010 Chinese New Year). “Until quite recently, the attitude has been, ‘Let’s invent in the West and ship to China’,” says Hubert Hsu, head of Boston Consulting Group’s consumer practice in China. “It didn’t work.”
[ Newsweek “Made for China” Oct. 10, 2010 ]
Ferrari developed a “China Limited Edition” 599 GTB Fiorano—only manufacturing 12 of the Chinese-only models. It was followed by a super limited-edition—a unique model (only one car made)—which was bought by a Shanghai bidder in an auction for nearly US$2 million.
[ Wired Mag. “Ferrari Makes One For China” Oct. 9, 2009 ]
Q: How much did a Chinese bidder pay for a bottle of wine at auction to break the world’s record in 2011? Find out in China facts: CHINA CONSUMPTION & THE CHINESE CONSUMER.
NEXT: China Facts: HEALTH, OBESITY & SMOKING >>
Return to Facts about China home page