Rapid industrial development and the dominance of economic growth in political considerations have taken a major toll on the environment and air quality in China. This includes major pollution in China, energy crises and more.
I’d like to share with some of the important facts and statistics related to pollution in China and the environmental impact.

These China facts and figures will be organized by the following categories.
- China’s Energy Consumption
- Pollution in China
- China’s River & Water Crisis
- China’s Green Economy and Future
- China’s Alternative Energy Solutions
- China’s Forests and Reforestation
Click on the links above to jump to that particular section, or continue to scroll down to browse these fascinating and alarming China facts and statistics.
Facts: China Energy Consumption
The following are some staggering facts related to China’s energy consumption over the past few years.
Since 2011, China has consumed more coal than the rest of the world combined.
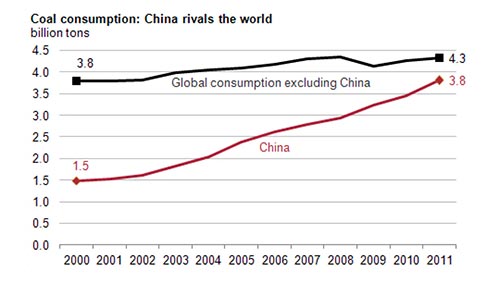
For decades, China has steadily been increasing its coal consumption until, in 2011, its consumption met the sum total of the rest of the world combined.
They’ve since attempted to curb their reliance on coal, but it is still the single-greatest source of energy for China.
China is the world’s biggest energy consumer
This came after topping the U.S. in 2009 according to the International Energy Agency.
However, the U.S. is still by far the biggest per-capita energy consumer, with the average American using five times as much energy as the average Chinese.
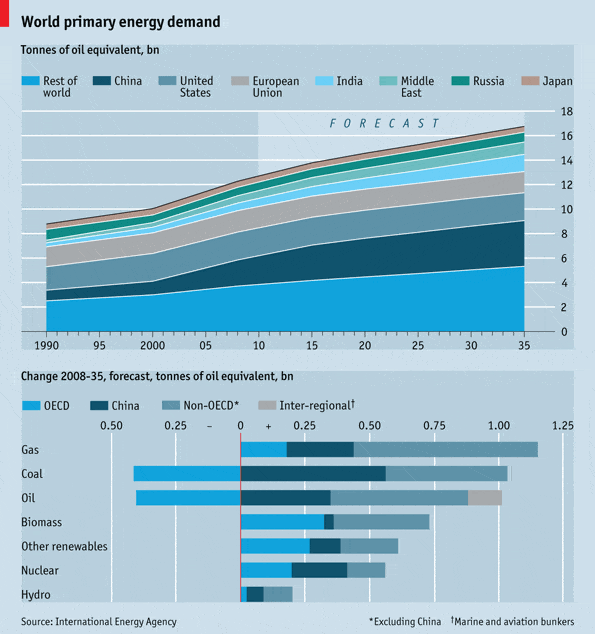
Source: Wall Street Journal
China’s electricity consumption is expected to increase 66%
It is expected that China’s electricity consumption will increase 66% between 2019 and 2023. This is based on trends over the past decade in addition to forecasts.
Coal still remains the primary source of this electricity, however, which further solidifies China’s reliance on coal as an energy source.
Source: ZDnet
China imports more oil than any other country
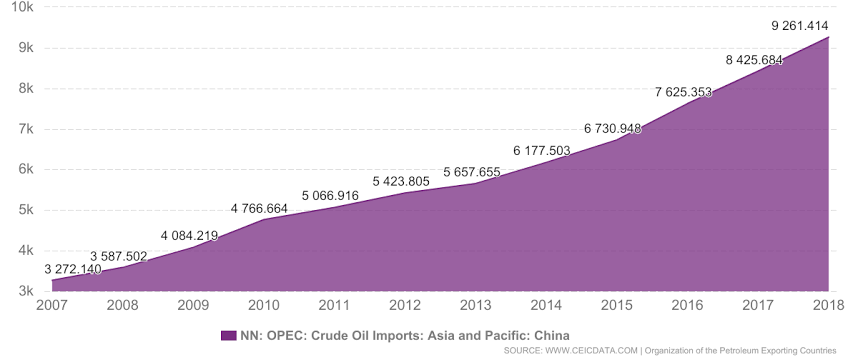
Year after year, no other country in the world imports as much oil as China does. In 2018, China represented more than 20% of all crude oil imports.
The country continues to develop its own crude oil extraction and refinement in places like Xinjiang and Inner Mongolia, but these can’t seem to keep pace with China’s growing demand for oil.
China’s Three Gorges Dam generates 20x more power than the Hoover Dam
First put online in July of 2012, the Three Gorges Dam is a massive energy generator for the region. It creates 20x’s as much hydro electricity as the Hoover Dam does!
Although the dam has been criticized for its insane costs and environmental toll on the area, there’s no denying that it’s a huge energy producer.
Source: Wikipedia
Facts: Pollution in China & Climate Change
Everybody is aware of the problematic pollution in China. Some cities in China are famous for their insane levels of smoggy air. Here are some facts to back up the stories you’ve heard.
China is the world’s largest producer of carbon dioxide emissions
China passed the US for this distinction in 2006, according to the Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency.
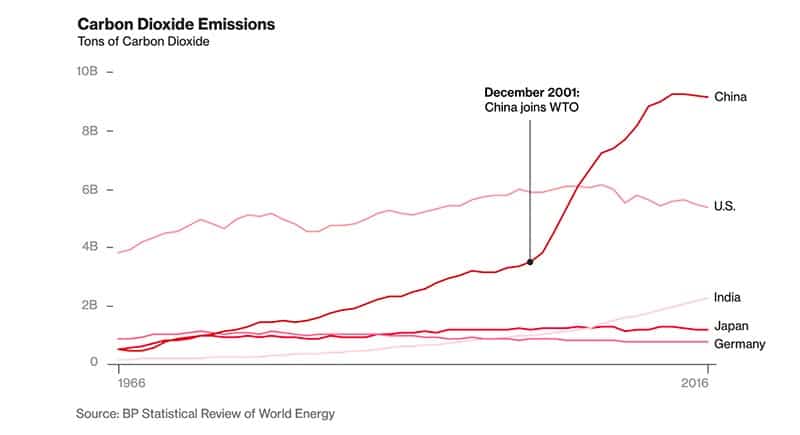
These carbon dioxide emissions have begun to fall again, but there’s still a large gap between China and the U.S.
Source: Bloomberg
Pollution is blamed for 1.6 million deaths in China per year
In 2015, it was estimated that an average of 1.6 million deaths in China were directly attributed to the high pollution levels in the country.
The research, which was done by Berkeley Earth, concluded that this total constituted 17% of all deaths in China for the year.
China is home to 22 of the world’s 50 most polluted cities
Cities in India are racing to catch up, but China still has a firm grasp in this top 50 most polluted cities. A simple glance at the average PM2.5 levels during a winter day in China is a good example.
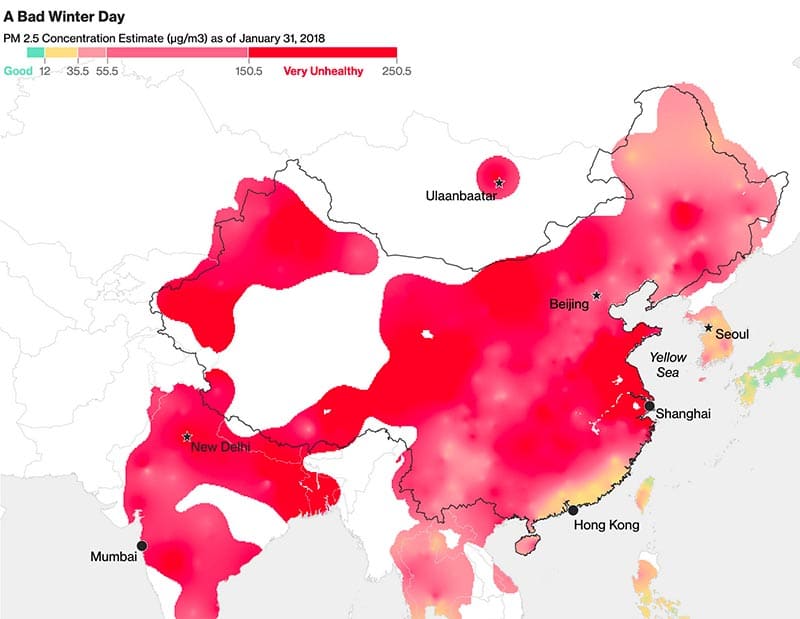
With the exception of large, uninhabited spaces in the deserts of Xinjiang and the steppe of Tibet, pretty much every corner of China has to deal with dangerous PM2.5 pollution levels.
Source: AirVisual
China car emissions are choking its residents
Back in 2005, auto emissions accounted for 79% of China’s total air pollution (via China: The Balance Sheet).
While emissions are still a bit problem in China, thankfully new regulations and standards have begun to change how things are done in the country. So strict are these regulations that Chinese car manufacturers had to halt production of 500 types of vehicles that didn’t reach these standards.
China’s Polluted Rivers & Water Crisis
The pollution in China isn’t limited just to the air. They are battling this problem in another important place: their rivers and water sources.

85% of China’s groundwater is rated as “bad” or “very bad”
According to a 2018 study by China’s Ministry of Ecology and Environment, only 10% of China’s groundwater stations reported “good” or “excellent” water quality.
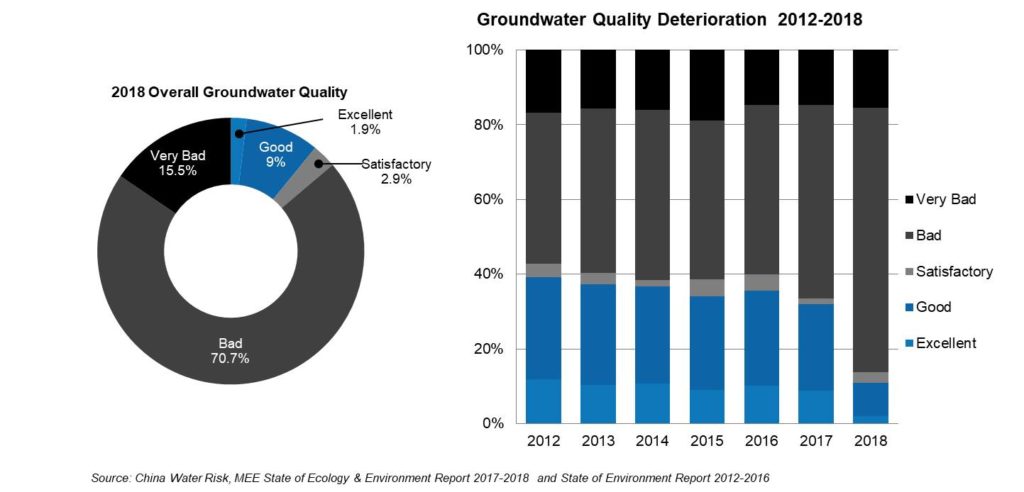
These numbers are alarming by themselves, but even more so when you see that it’s a downward trend.
Source: China Water Risk
China’s water supplies will be completely exploited by 2030
Surprisingly, this fact was shared by the Chinese government itself in an effort to get all of its officials and population on board with new water standards.
Another related and interesting fact: China holds 7% of the planet’s water resources to care for 20% of the world’s population. It’s no wonder they’re having such a problem!
Source: Reuters
In Beijing, 39.9% of water is so polluted that it’s essentially useless
This 2017 report by Greenpeace showed this water pollution was a problem not only in China, but also in many other cities across the country.
Despite efforts to improve the water quality, almost half of China’s provinces have failed to hit their quality targets.
China’s Future “Green Economy”
In spite of all these fairly negative numbers and statistics, it’s fair to say that China is leading the way for the world’s move toward a more “green” economy.
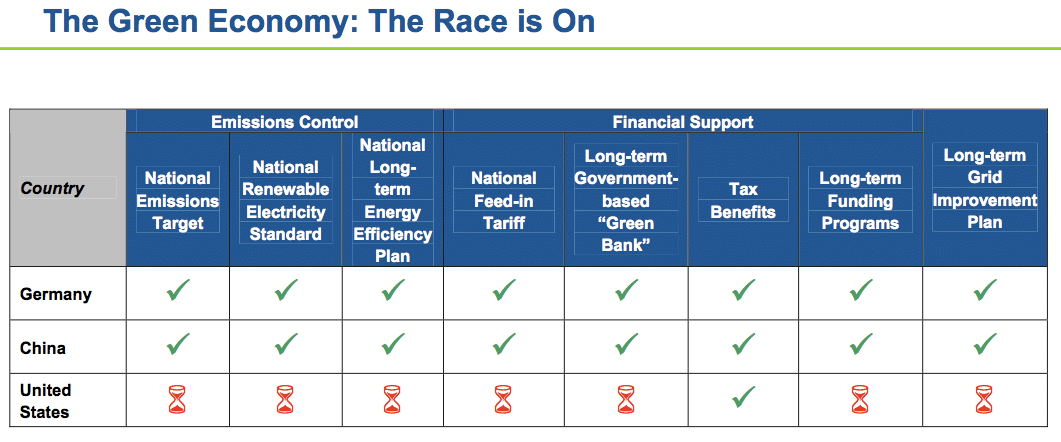
China is investing $75 Billion/Year in clean economy measures
China’s 10 year plan ending in 2020 expects to spend between $75 to $100 Billion US dollars per year on clean energy projects.
These projects include reducing emissions, developing new cleaner energy sources and putting more electric vehicles on the road.
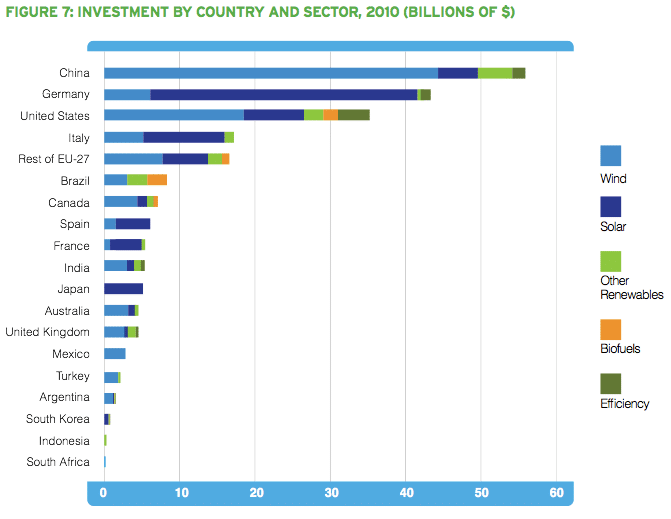
Source: Harvard Business Review
Chinese consumers buy 3x’s more electric vehicles than US consumers
Over the past few years, China’s electric vehicle market has soared past any other country in the world, including the United States.
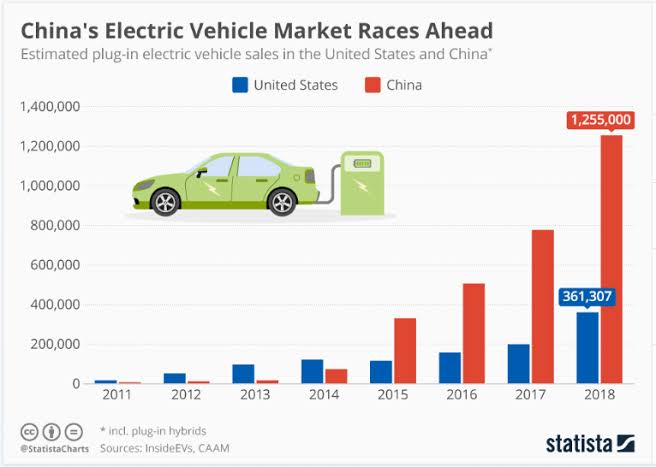
China has the ambitious goal of having 12% of its consumer vehicles be electric by 2020. It’s a target that it probably won’t hit, but they’re getting amazingly close.
Source: Thailand Business Review
China’s Alternative & Clean Energy Technology
As part of its efforts in clean energy, China has invested heavily in alternative energy sources and technology. Here are just a few.
In 2010, China became the world’s largest wind energy producer…
…and since that time it has left the global competition in the dust.
Wind farms in Gansu, Xinjiang, Inner Mongolia and other provinces have been popping up like crazy and in many cases, their energy production outpaces what can be used and/or stored.
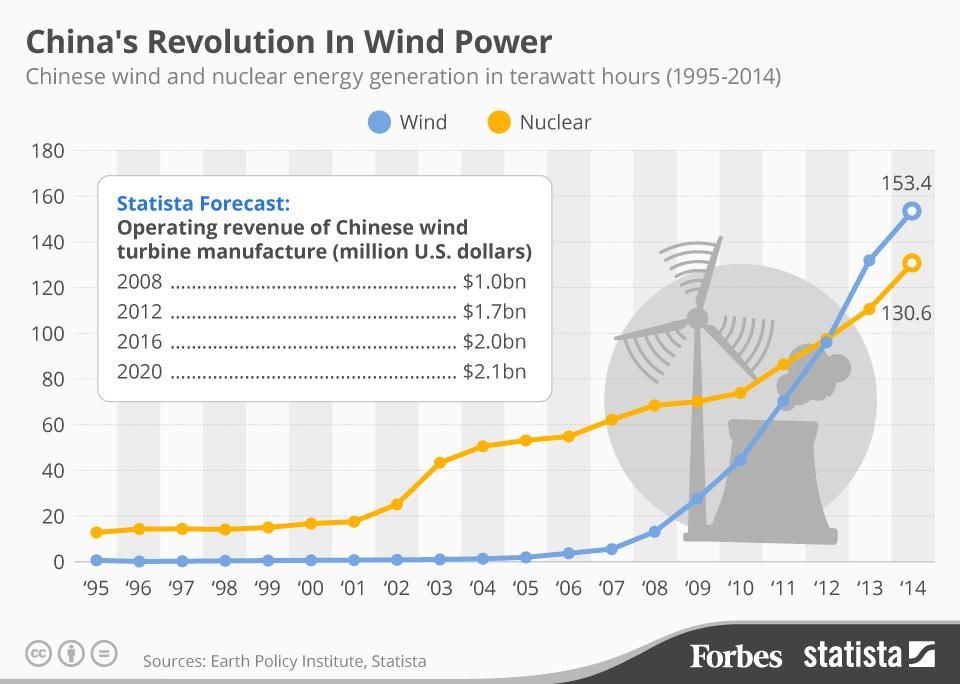
Source: Forbes
By 2024, China will have 2x the solar capacity of the US
It’s crazy to imagine that about two decades ago, China had little to no solar panel farms. In that short span of time, it has rocketed to become the leader in the world.
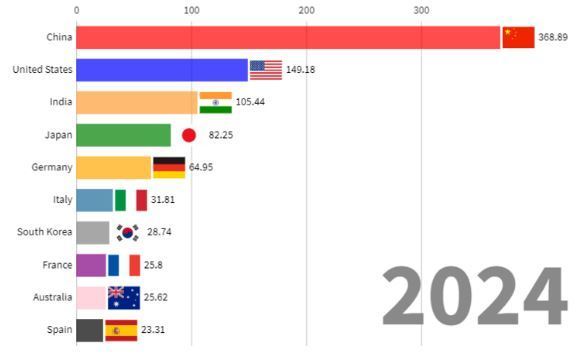
It already leads the way in solar installs, but projections estimate that by 2024, it will be double that of the nearest country, which is the United States.
Source: Solar Feeds
China adds one new nuclear reactor every 5 months
Although China currently lags far behind countries like the United States when it comes to nuclear reactors and the power generated by those nuclear plants, the trend shows this will be changing soon.
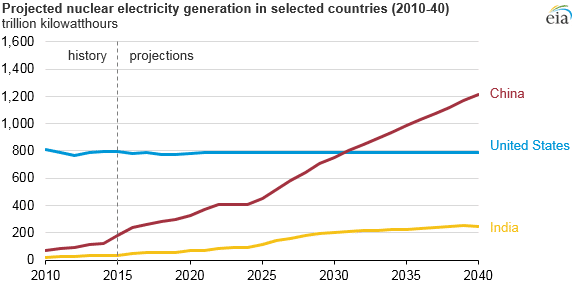
At the rate of one new nuclear reactor every five months, China will easily overtake the United States in terms of nuclear power generation by 2032.
Source: US Energy Information Administration
China’s Forests & Reforestation
China is dealing with plenty of desertification and fighting it with reforestation.
China is home to 4% of the world’s forest area
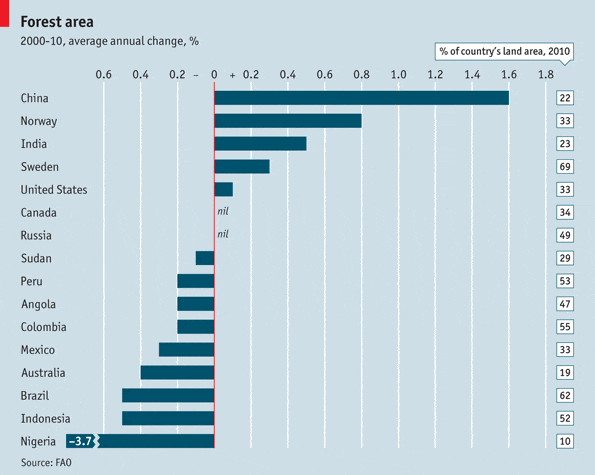
- China possesses about 4% of the world’s total forest area. [“China: Asia in Focus”, R. LaFleur 2010]
- China’s forest cover increased from 12% to 18% in two decades (1990-2010), through vigorous reforestation programs. The government has a national goal of reaching 23% by 2020. [“China: Asia in Focus”, R. LaFleur 2010]
- China increased their forest coverage between 2000 and 2010, at an average annual rate of 1.6% (despite overall worldwide deforestation). [The Economist online “The World’s Forests” Feb. 11, 2011 ]
- Launched in 1978, China’s “massive tree-planting scheme” is expected to cover 400 million hectares (or 42% of China’s landmass) by 2050, which would be “arguably the biggest man-made carbon sponge on the planet.” [Guardian UK “China’s loggers down chainsaws in attempt to regrow forests” March 11, 2009]
- Over the past three decades, Chinese volunteers have planted about 58.9 billion trees across the country, according to statistics from the State Forestry Administration. [China Daily “Chinese leaders join in tree planting campaign” April 2, 2011 ]
- China uses and throws away 45 billion disposable chopsticks every year, representing about 25 million trees.[Wikipedia; China Daily, “Call to abandon wooden chopsticks” Aug. 10, 2007 ]




